
If multiple variables are declared, they should all be of the same type. In the initialization part, any variables needed are declared (and usually assigned values). This type of "semicolon loops" came from B programming language and it was originally invented by Stephen Johnson. It requires 3 parts: the initialization ( loop variant), the condition, and the advancement to the next iteration. Some languages require a separate declaration of the control variable, some do not.Īnother form was popularized by the C programming language.
An optional step-value (an increment or decrement ≠ 1) may also be included, although the exact syntaxes used for this differs a bit more between the languages. last do statementĭepending on the language, an explicit assignment sign may be used in place of the equal sign (and some languages require the word int even in the numerical case).

The name for-loop comes from the word for, which is used as the keyword in many programming languages to introduce a for-loop. For-loops can be thought of as shorthands for while-loops which increment and test a loop variable. For-loops are typically used when the number of iterations is known before entering the loop. The header often declares an explicit loop counter or loop variable, which allows the body to know which iteration is being executed. There are other possibilities, for example COBOL which uses "PERFORM VARYING".Ī for-loop has two parts: a header specifying the iteration, and a body which is executed once per iteration. Various keywords are used to specify this statement: descendants of ALGOL use "for", while descendants of Fortran use "do".
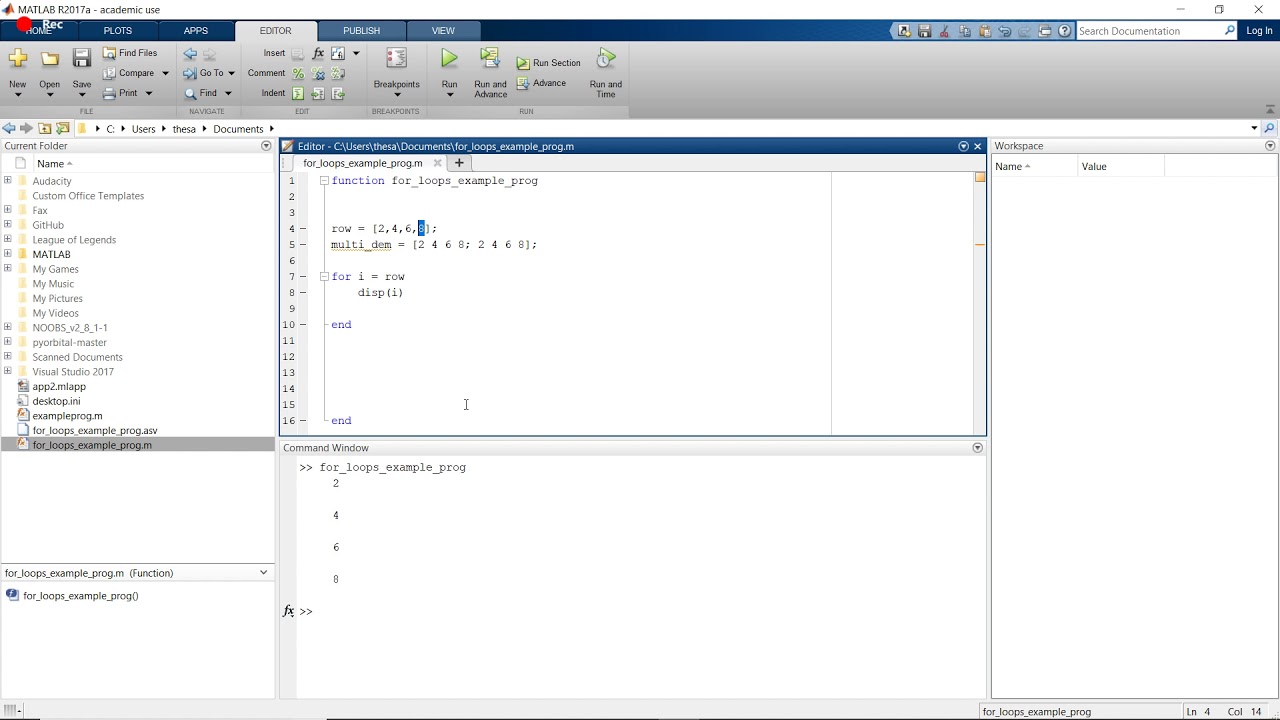
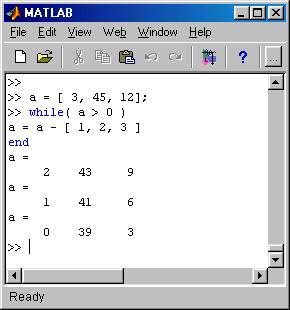
FOR LOOPS MATLAB CODE
In computer science, a for-loop (or simply for loop) is a control flow statement for specifying iteration, which allows code to be executed repeatedly.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
